What are the PCB hole types?
20 January 2025
Views: 1171
Circuit boards have different holes for specific purposes. These holes include through holes, copper holes, copper-free holes, blind holes, buried holes, countersunk holes, positioning holes, and reference holes. Each hole has a different function.
1. Through holes
A through hole is a small cylindrical opening that runs through all layers of a PCB. It is used to connect different layers of a circuit board and promote vertical transmission of signals and power. It not only provides a channel for electrical connection, but can also be used as a mounting point for components. Depending on whether the hole wall is copper-plated, through holes can be divided into copper holes (PTH) and non-copper holes (NPTH).
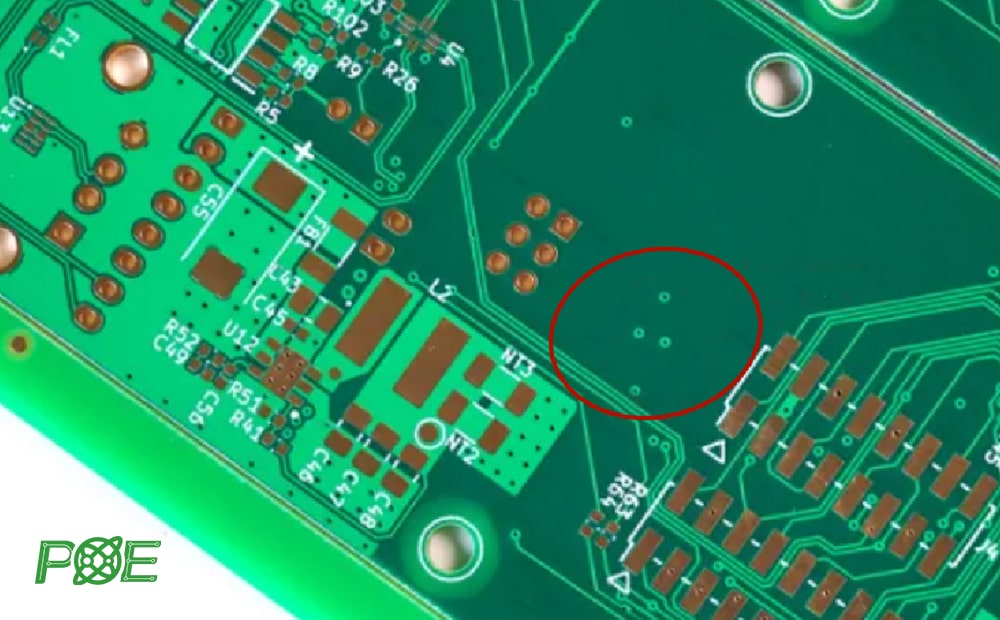
2. Copper holes
Copper holes (PTH) are special through holes that use electroplating technology to deposit conductive materials on the hole wall, and the thickness is usually 20-25 microns.
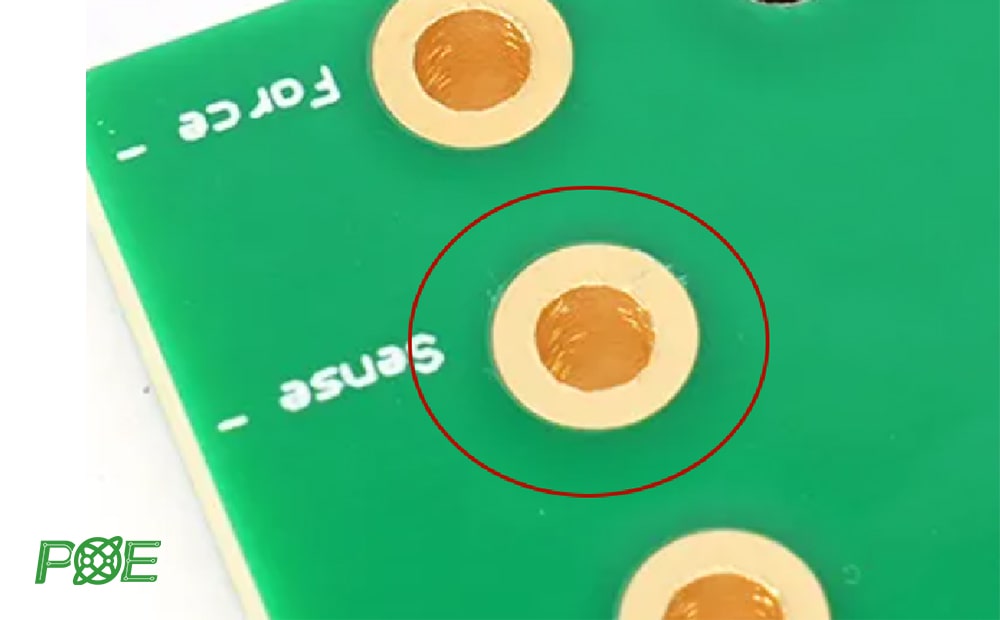
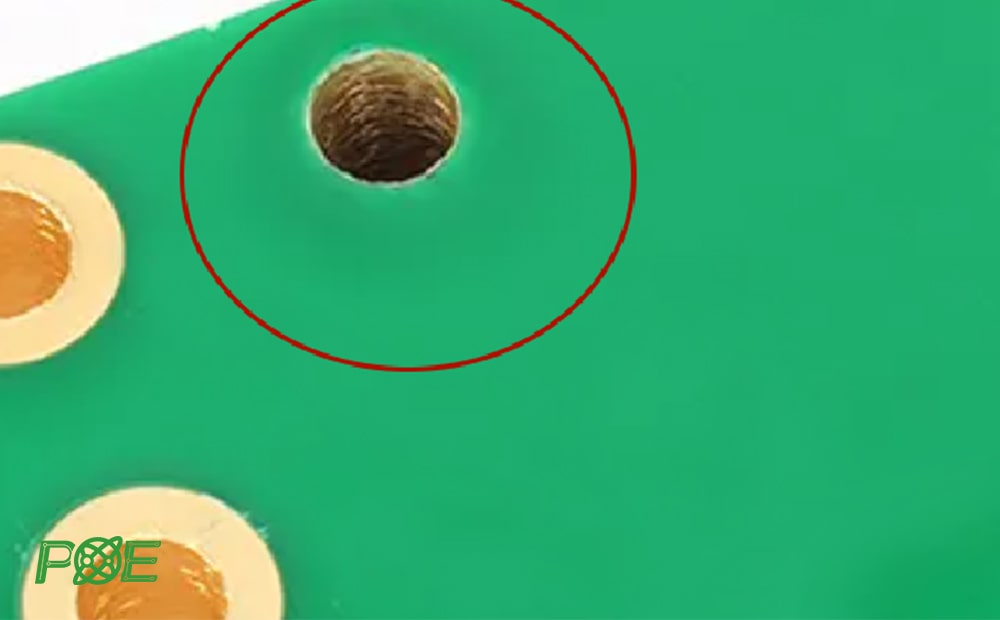
3. Non-copper holes
Non-copper holes (NPTH) are mechanically drilled holes that are not copper-plated. Although non-copper holes do not have conductive functions, they have important functions. Non-copper holes are often used to install fixing screws.

4. Blind holes
A blind hole is a special interconnection hole that penetrates from one side of the PCB to a certain layer inside. Blind vias are particularly valuable in HDI. However, blind vias are expensive to make and require special electroplating processes.
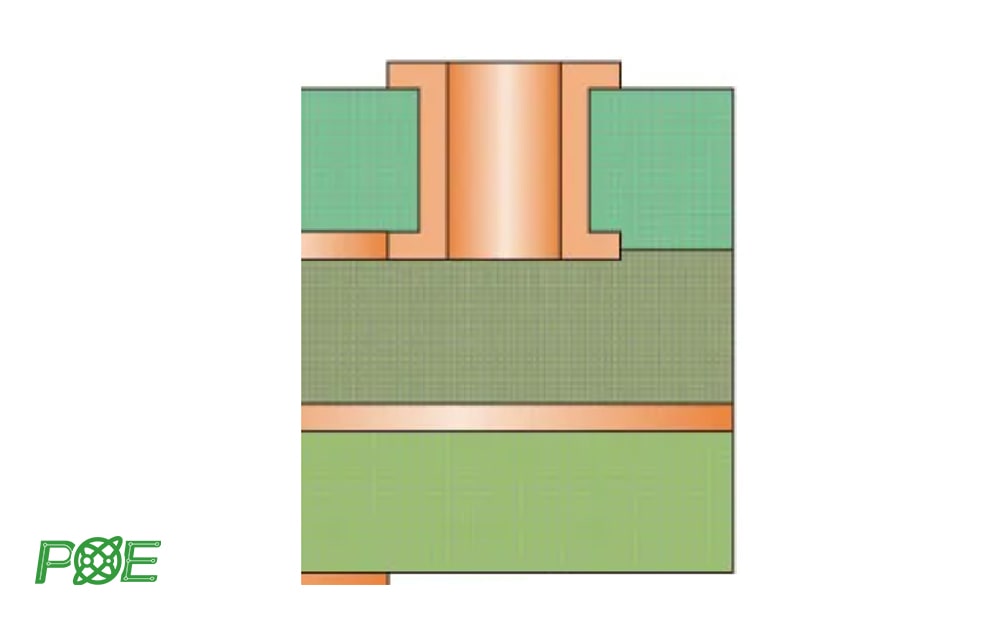
5. Buried vias
Buried vias are interconnected holes that are completely enclosed inside the PCB. The inner layer connection does not lead to the outer layer. The production of buried vias requires multiple pressing processes, which has high requirements for materials and processes. In high-frequency circuits, buried vias can reduce electromagnetic interference and improve signals.
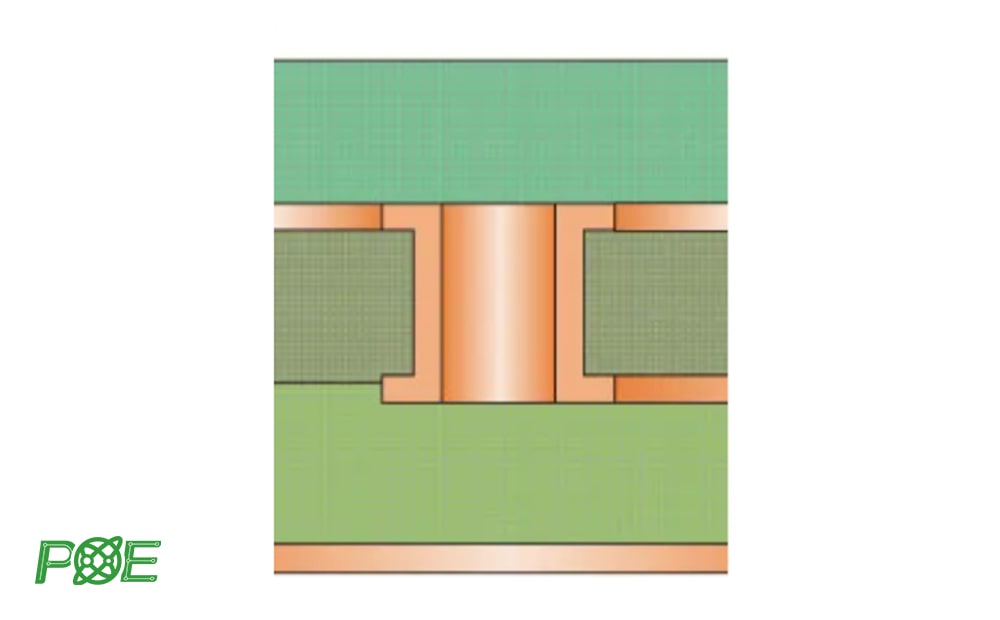
6. Countersunk holes
Countersunk holes are mechanical holes with a special shape, with a cone on the upper part and a straight through hole on the lower part. This design is mainly used to accommodate flat head screws.
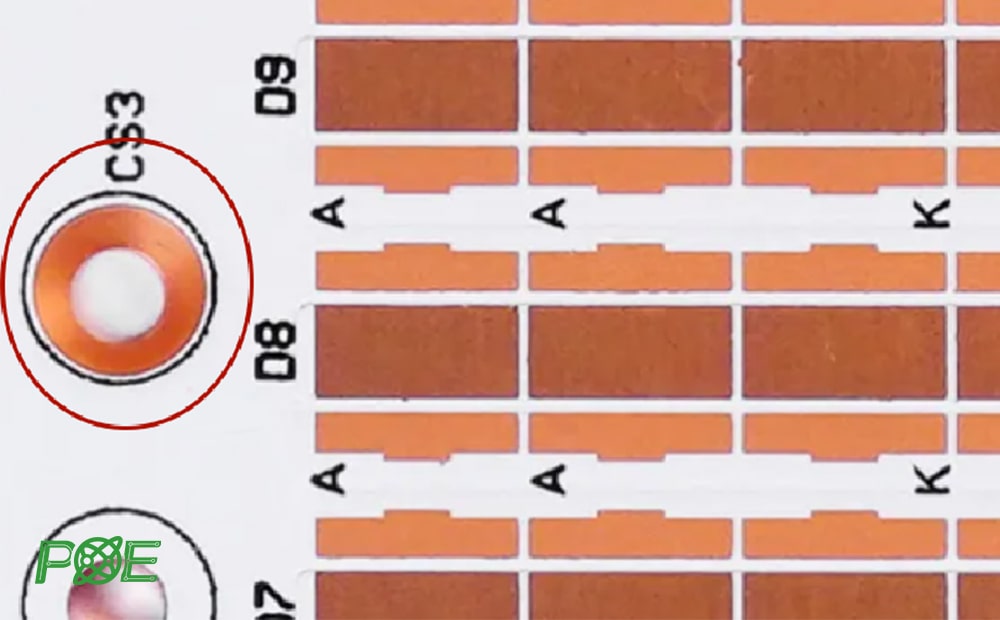
7. Positioning holes
As the name suggests, positioning holes are holes used as references for precise positioning. The position accuracy of the hole is required to be within 0.1mm. Positioning holes play an important role in production accuracy, PCBA, testing and rework processes.
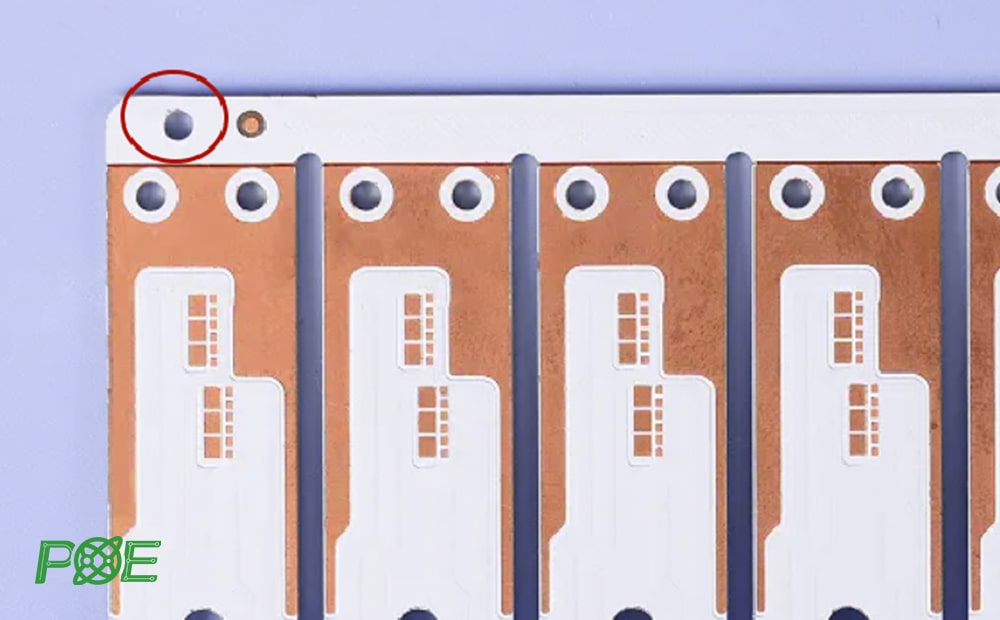
8. Reference holes
The reference hole is a special positioning mark used for automated assembly and optical inspection. In the SMT process, the reference hole is an important reference point to ensure the precise placement of components. At least three points need to be set on the PCB to form a stable positioning reference system that can be accurately recognized by the machine under different lighting conditions.
Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!