PCB assembly is the process of mounting electronic components onto a PCB to make it functional. Various components are used in this process, each with a specific purpose to ensure the circuit runs smoothly.
1. Resistors
Resistors are one of the most basic components in PCB assembly. Their main function is to limit the flow of current in a circuit. By converting electrical energy into heat, resistors can regulate voltage and current, ensuring that other components can operate safely without overloading.

Common types of resistors
Fixed resistors: provide a constant resistance value.
Variable resistors (potentiometers): allow the resistance to be adjusted.
SMD resistors: compact resistors designed for surface mount technology.
2. Capacitors
Capacitors store electrical energy, stabilize voltage and filter noise in circuits, and are often used with resistors in timing circuits.

Types of capacitors
Electrolytic capacitors: high capacitance, commonly used in power circuits.
Ceramic capacitors: small and versatile, suitable for high-frequency applications.
Tantalum capacitors: known for their stability and reliability.
3. Diodes
Diodes are components that allow current to flow in one direction only, acting as electrical "check valves" and are often used for rectification, converting AC to DC, and protecting circuits from voltage spikes.

4. Transistors
Transistors are semiconductor devices used for amplification, switching, and signaling, creating logic gates in digital circuits and amplifying weak electrical signals in analog circuits.

Types of transistors
Bipolar junction transistor (BJT): used for switching and amplification.
Field effect transistor (FET): often used in low-power applications.
5. Integrated circuits (ICs)
Integrated circuits are small chips containing transistors, resistors, and capacitors, all in one package, that enable functions such as computing, signal processing, and memory storage.

Examples of ICs in PCB assembly
Microcontrollers: small computers on a chip, used in embedded systems.
Operational amplifiers (Op-Amps): used for signal amplification.
Digital signal processors (DSP): used for high-speed signal processing.
6. Inductors
When current flows through them, they store energy in a magnetic field. They are often used in power circuits, filters, and transformers to manage energy transfer and reduce interference.

7. LEDs
LEDs are light-emitting diodes that are used as indicators and for lighting in many applications.

8. Switches
Switches are electronic components used to turn circuits on and off, allowing users to control the flow of current, turning devices on or off as needed.

Common switch types
Toggle switches: simple on/off mechanisms.
Push button switches: for momentary or latching operation.
Rotary switches: allow selection between multiple options.
9. Connectors
Connectors are used to connect different parts of a circuit, ensuring a stable electrical connection and allowing easy assembly and disassembly.

Connector examples
Pin headers: commonly used for internal connections.
USB connectors: allow external devices to interface with PCBs.
Coaxial connectors: used for high-frequency signal transmission.
10. Crystals and Oscillators
Crystals and oscillators provide clock signals to synchronize operations in digital circuits and are critical in devices such as microcontrollers and microprocessors.

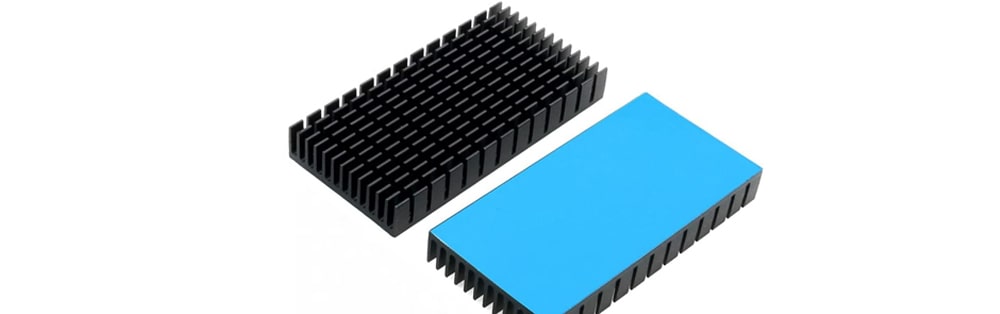
11. Heat Sink
Heat sinks are used to dissipate heat generated by components such as transistors, ICs, and power regulators to prevent overheating.
12. Battery
Batteries power circuits, especially in standalone devices, and are often integrated into PCB designs along with power management circuits.

13. Transformer
Transformers transfer electrical energy between two circuits through electromagnetic induction and are used in power circuits to increase or decrease voltage.

Conclusion
PCB assembly requires a variety of components to be combined into a fully functional PCB, each with unique functions.













